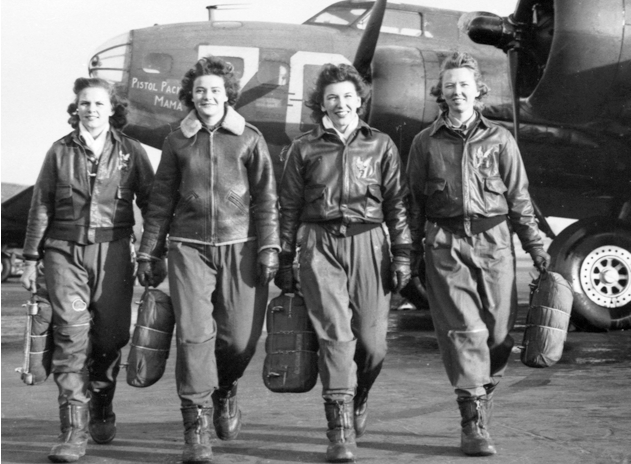
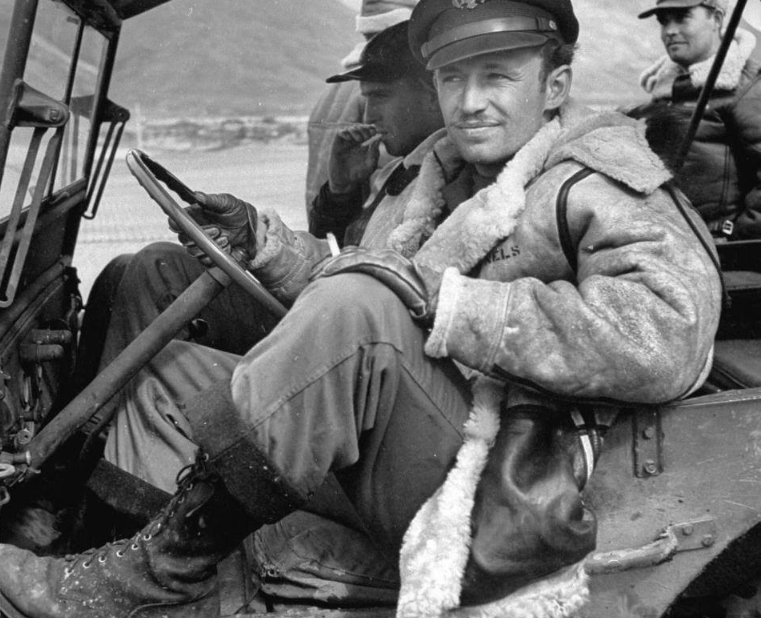
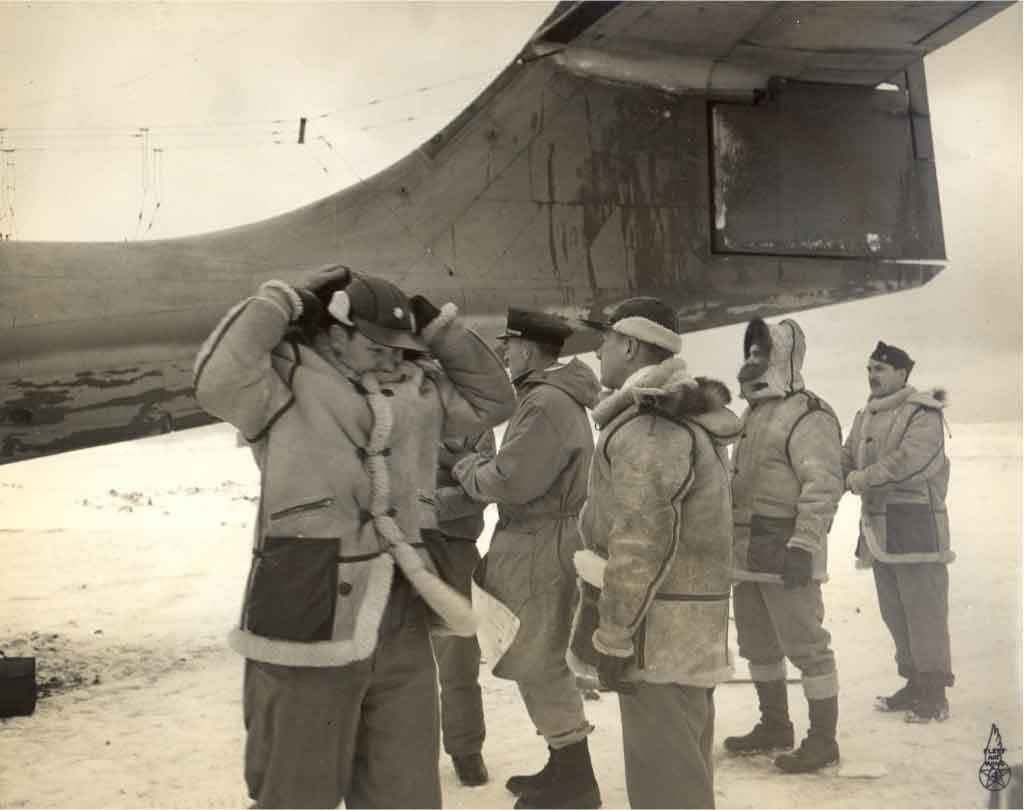
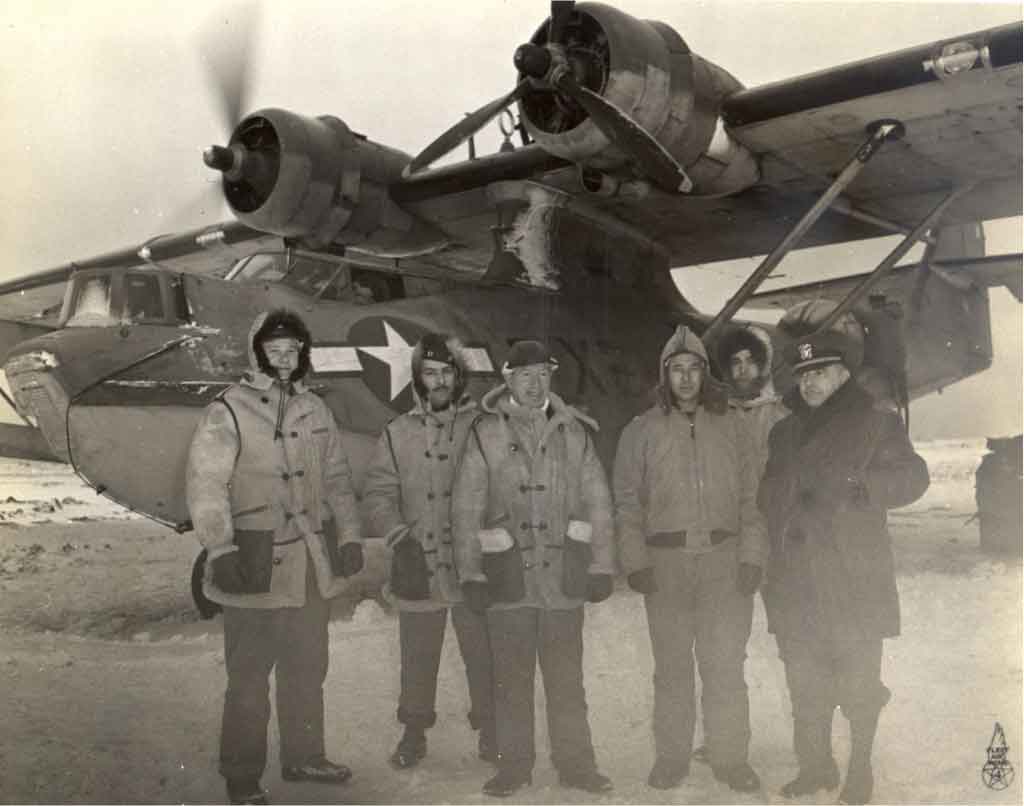
THE HISTORY OF FLIGHT JACKETS
The bomber and flight jackets were first produced with an intention of providing some lightweight work wear that would be suitable in every way for the military personnel. They have a timeline record which shows the changes in style and modifications that have occurred in their design. Flight jackets have seen design modifications from the time of invention when they were mainly produced for use by the military men, to contemporary times where they now qualify for use as cool casual outfits for almost anybody.
At AVI LEATHER we have done our best to create a compilation of the some of the most important flight jackets that have been, together with their basic descriptions and some illustrations.
A1 JACKET (1927)
The A1 jacket was the first produced flight jacket; it was manufactured in 1927 by different company makers. The fact that it had multiple producers resulted in varying product descriptions, but even still, they had common essential features that unified them. Although they are comparatively simple to the others, it’s value and prestige at the time of its use was enormous. Their relevance remained even during the second world war; some fourteen years after the better-designed A2 bomber jacket had been produced. Their official and formal use came to a stop after the A2 jacket was made in 1931.
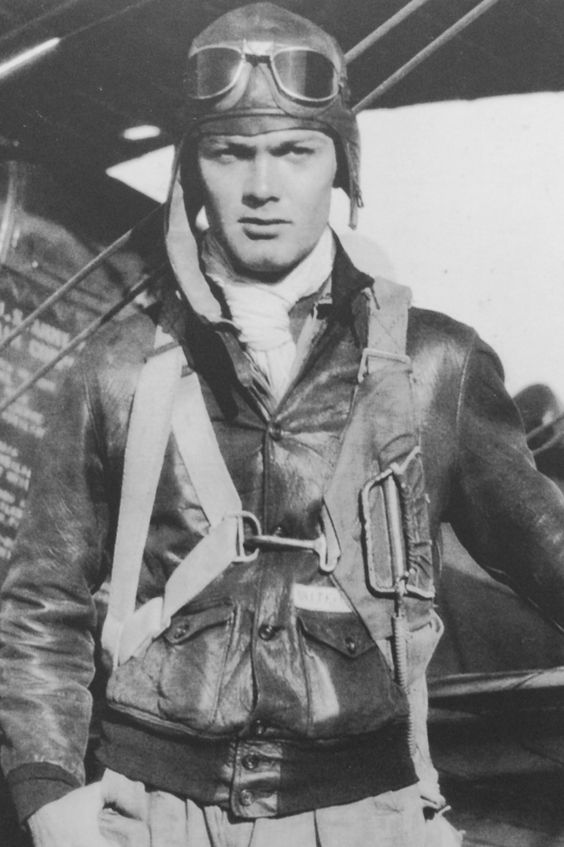
A2 JACKET (1940)
Initial designs for the A-2 Flight Jacket arrived in the early 1930s, evolving from the A-1. The A2 flight jackets were created mainly out of horsehide or goatskin. The A2 jackets were designed with heavy duty fasteners, cuffs and knit waists. Both of the A1 and A2 jackets have similar cuts, but unlike the A1 jacket that had buttons, the A2 were fitted with sturdy zippers instead. The addition of the zippers and collar to the A2 would have contributed to the sophistication and smartness it had over the A1 jackets. The A2 stayed in vogue until 1943 when fewer people began to use it. But even still, its significance cannot be forgotten by those who knew.
B3 JACKET (1934)
The B3 flight jacket was designed for aircraft bombers who needed to go up high altitudes. Thus it could be rightly referred to as the ‘bomber jacket’. The material composition are a combination of sheepskin and very thick sheep fur. The jackets were not meant to be just the regular types, as they were intended to keep people warm at an altitude of up to 25,000 feet. Thus earned the jacket its reputation as one that was capable of providing sufficient warmth. Each of the jackets had two leather straps that could be used to close the open collar; but unlike the other jacket type, B3 jackets did not have a knit waist band or a trim fit.
D1 JACKET (1937)
This leather jacket was designed to be used by personnel who had to work under terrible weather conditions but whose work did not involve flying. The D1 jacket was of simple design, granting the user a reasonable ease of movement, while still protecting them from the cold weather. The D1 jacket was later used by pilots who found it useful because of the purpose and convenience it served. So, instead of been reserved solely for use by the ground crew, it became a useful clothing addition for the pilots who usually used it alongside the A2 jackets in a bid to conserve warmth.
B6 JACKET (1939)
The B6 flight jacket was first produced at around 1943; just about the same time the B3 jackets were also very much in use. The jacket came as some improved version of the B3 jacket. A difference between the B6 and the B3 is its relatively light weight. The need to create this type of flight jacket would have garnered support at the period just before the start of the war, because the available fighter aircraft’s at that time lacked heating facilities. Notable among them, is the P38 air fighter that did not seem to have any heat generating ability.
B7 JACKET (1941)
The B7 jackets also known as the B7 arctic parka was produced between 1941 to 1942 during WW2. It was produced specifically both for the flight crew and those working on ground in the debilitating cold and largely undeveloped areas. The jacket is a three-quarter length that proved effective against the harsh cold and snow storms. The material composition for the B7 jacket is shearing for its entirety, except for the hood that is lined with coyote fur. Due to the high cost of producing the jackets especially during the war, the continuous production if the B7 jacket could not be further sustained.
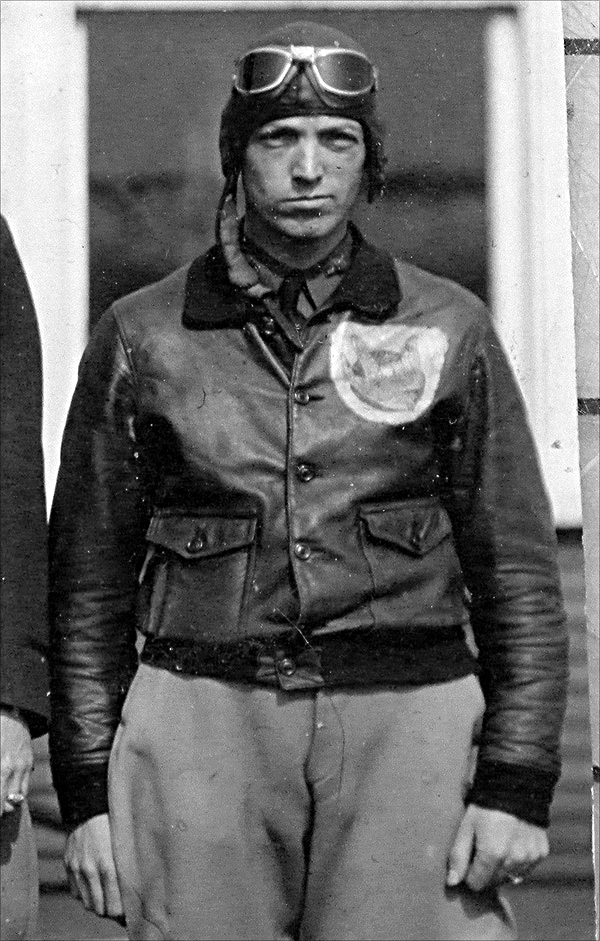
M422 AND M422a JACKET (1941)
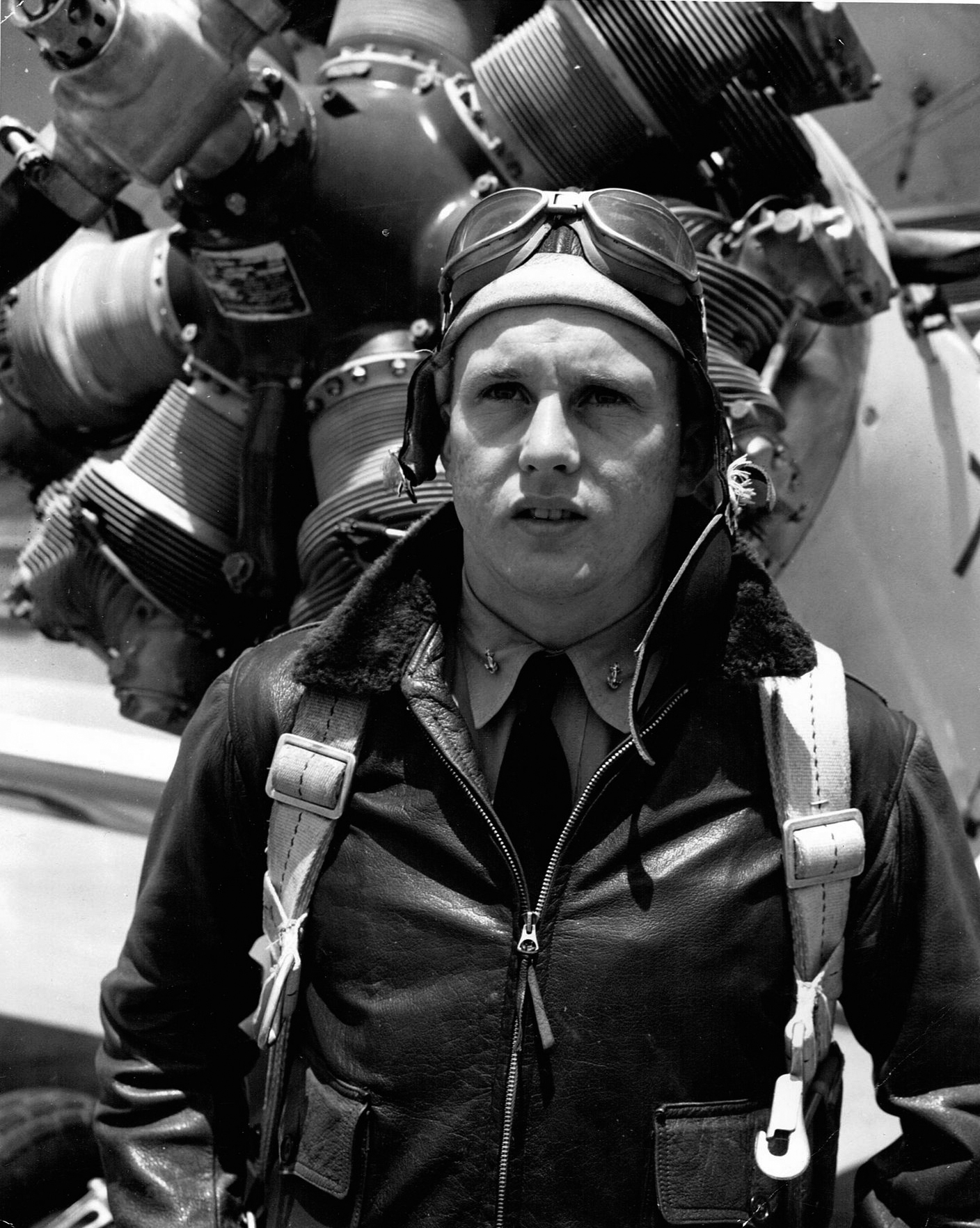
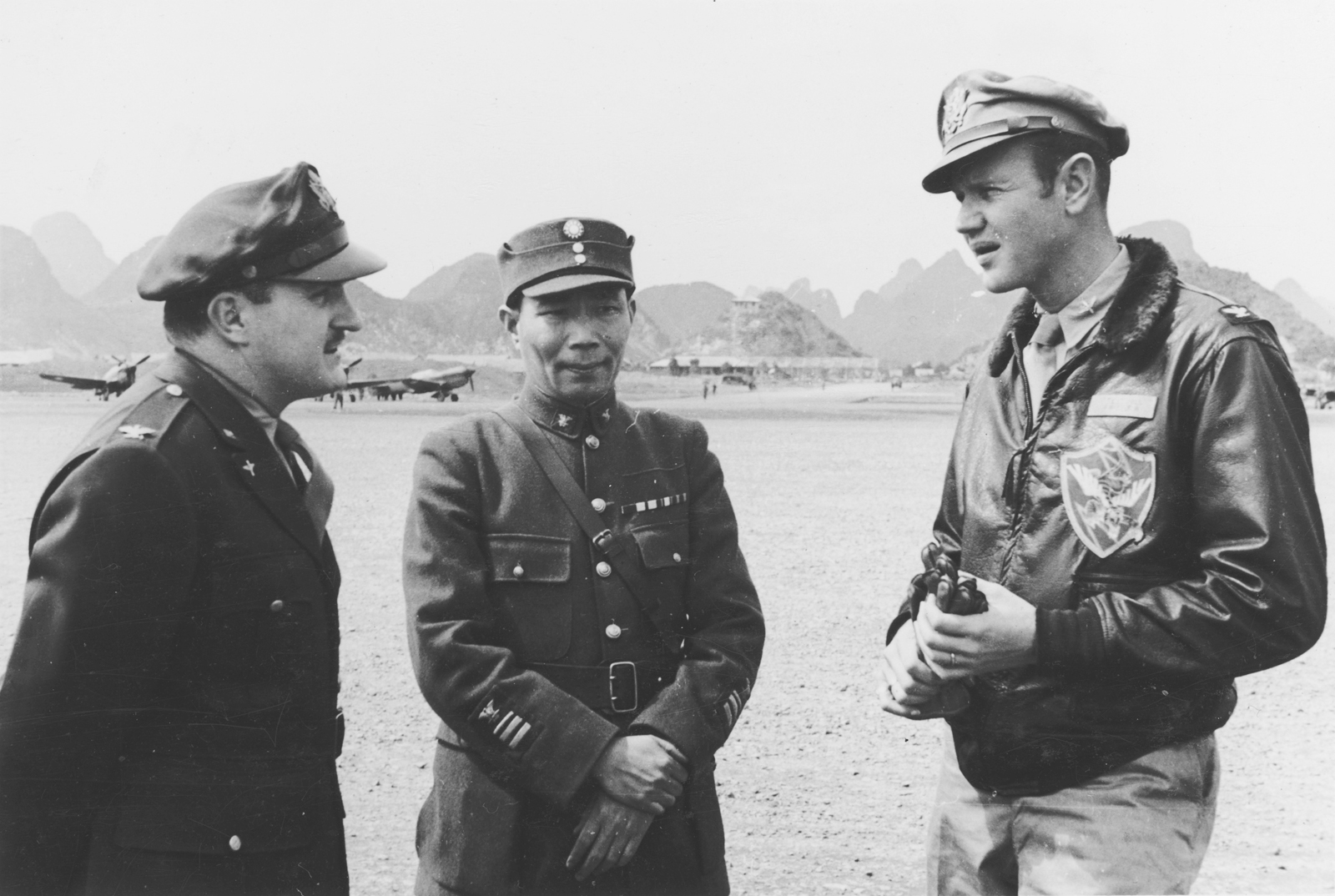
The difference between the M422 jacket and the M422a jacket was the addition of a pencil slot to the left side pocket of the M422a jackets. Up until 28th March 1940, the jacket was standardized by the US Navy’s Bureau of aeronautics and generally known as the M422. The M422a version of the jacket became officially recognized on the 1st of October 1941. In 1941 when American volunteers offered to assist the Chinese in the fight against the Japanese, the pilots who flew the P-40 shark mouth fighter aircrafts were provided with the M422a jackets which the National Chinese government had bought for the purpose.
G1 JACKET (1947)
The G1 jacket is a modified product of the M422a jacket. It has undergone series of testing and continuous standard modifications even up to contemporary times. But then, the jacket still maintains the basic designs and the production materials such as the goatskin, the mouton sheepskin, and the wool knit.
M422A JACKET VS. G1 JACKET
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE?
The M422A flight jacket and G-1 flight jacket may at first appear quite similar, so what if anything, is the difference?
The M422A was standardised by US Navy’s Bureau of Aeronautics on the 1st of October 1941. Later in 1947, the same basic design, with few small modifications, became standardised and re-designated as the G-1 jacket. So, the G-1 is more an evolution of the same design, with small details and spec changing.
The patterns of both leather jackets are very similar and varied from maker to maker, but both retained the bi-swing back, veg-tanned goatskin and mouton fur collar. Some subtle nuances may be apparent on closer inspection, but as with many things during this time period, there really was no hard and fast rule. So much depended on the various maker’s interpretation of the official USN specification.
M-422A jackets tended to have a slightly more relaxed pattern at first, compared to the next generation of G-1 jackets, but this is not always the case. Earlier G-1s like the 55J14 had wider shoulders and a very trim torso. In many cases the M-422A was slightly longer in the body than G-1s. M-422a jackets tended to have a slightly more “fuller” cut/ pattern, compared to the next generation of trim G-1 jackets.
Besides these slight pattern variations between contracts, one may notice that the collar of the G-1 became slightly smaller and more blunted. One may also notice the pocket flaps of G-1 designs becoming simpler and less classically shaped. Most of the M422a jackets had the “salmon red” rayon lining where most of the G1s used brown coloured lining.
One thing is for sure, whether you are drawn to the adventures of the AVG in China, the great air battles over the Pacific in WW2, the dogfights over Mig Alley in Korea, the carrier operations in Vietnam or if it’s the Tomcat tales of the 80s that you are most drawn too…
Whichever jacket you choose to take to the skies, rest assured that both jackets retain the classic pedigree of the original USN aviators from all of the most iconic periods in our recent history. Both jackets are extremely comfortable at the correct size, with the materials and quality being second to none. These are jackets that can be worn hard and enjoyed over lifetimes.
B10 JACKET (1943)
The B10 jacket was first produced in 1943 using cloth materials, but with it collar and lining made in alpaca fur. Although the designs looked more elegant than the ones before it, the B10 jacket did not seem to match the sheepskin products that were made before it, in terms of providing warmth. It resembles the G1 jacket with both of them having the same pocket styles and a zip closure without the wind flaps.
B15 JACKET (1944)
The B15 jacket was standardized on April 7th 1944. It came as some sort of alternative to the flight suits that were made of sheepskin. Although it retained some of the animal materials that were used for the previous models, it had a variety of different she’ll components which includes cotton-rayon combination as well as nylon. A new feature on the B15 jacket that has been adopted for a long time now, is the pen pocket on the left upper arm of the jacket.
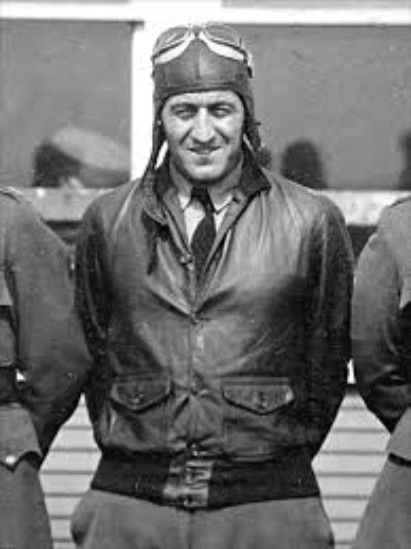
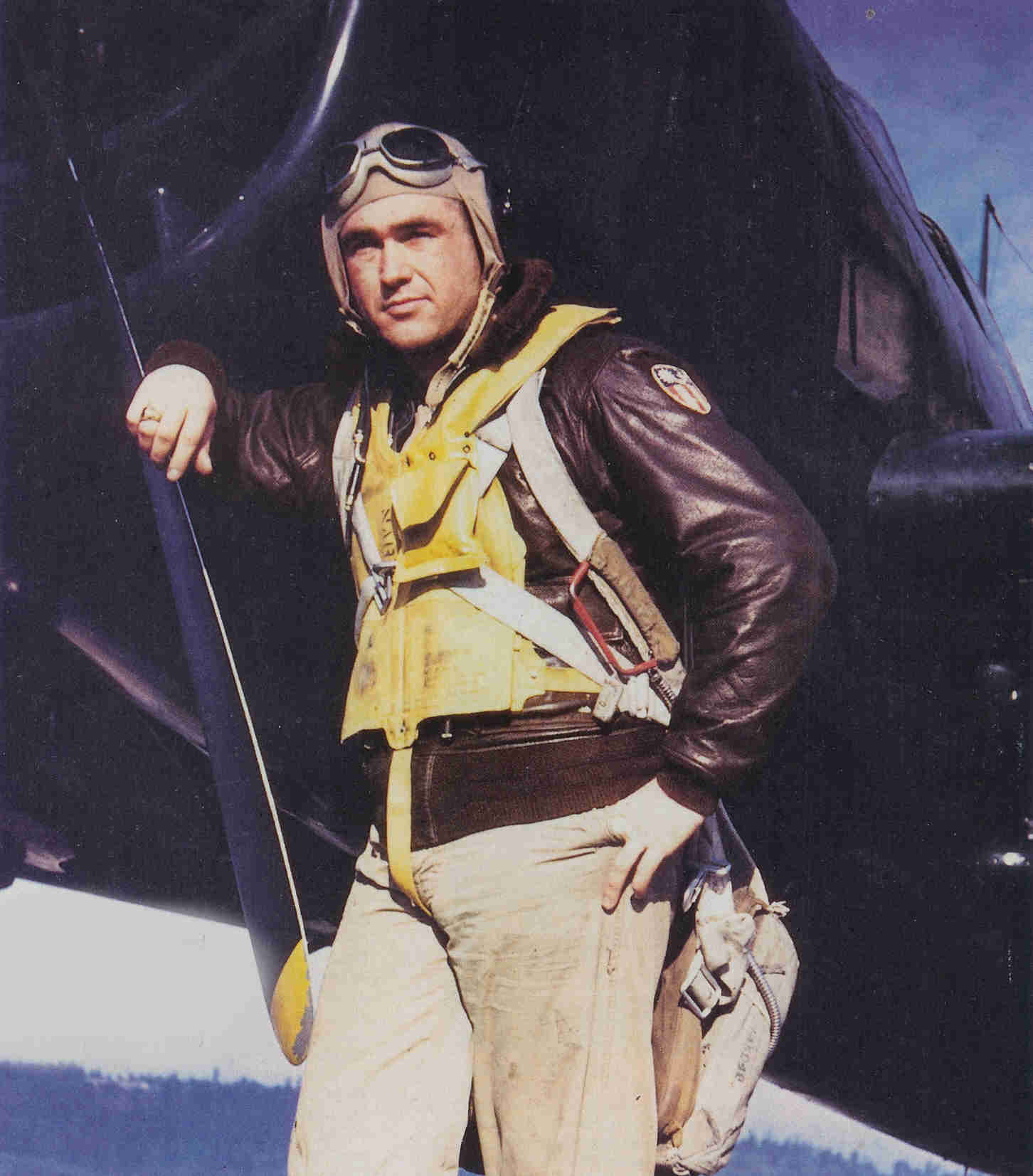
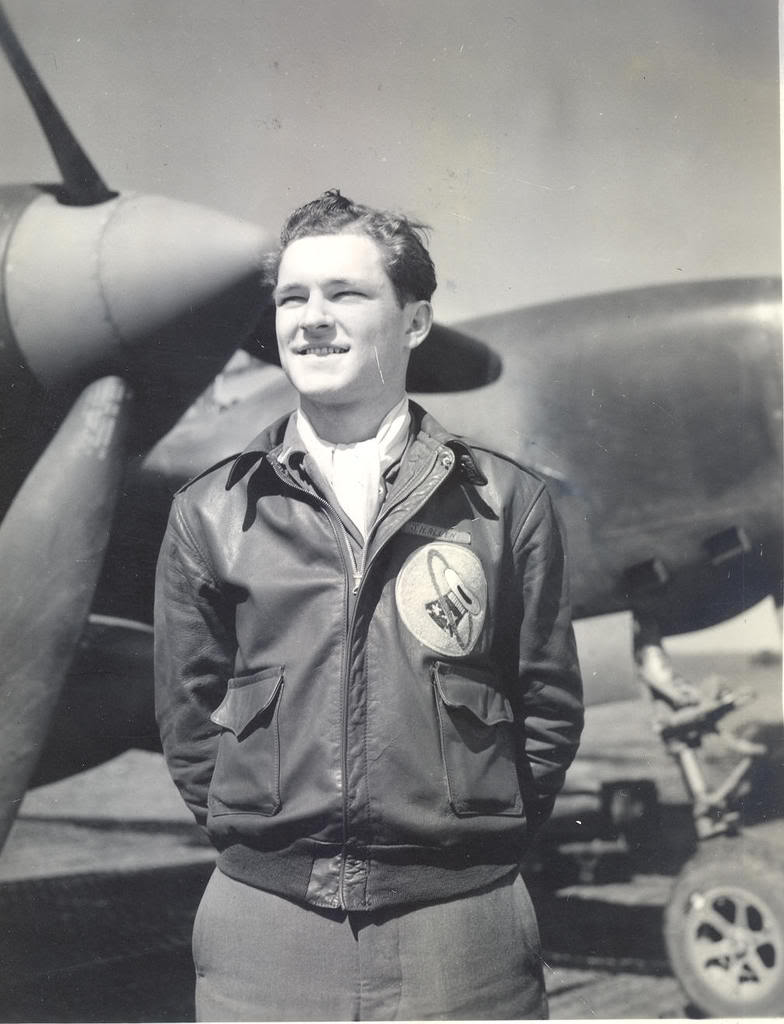
We are so proud to see Alfred Joseph Payne wearing our M-422A jacket.
He is the last survivor of USS Hornet CV-8! During the Battle of Midway, Alfred Joseph Payne was 18 years old and a Aviation Machinist Mate with Fighting Squadron Eight (VF-8). He was in charge of the propellers and helped launch the F4F Wildcats off the Hornet’s flight deck for that fateful mission. On October 26, 1942 during the Battle of Santa Cruz Islands, he witnessed the kamikaze hitting the island structure and was on the port side of the ship when the second bomber struck the bow. The crew was ordered to abandon ship and CV-8 was sunk.
Pictures and text from @georgeretelas